Web applications are now a important part of our everyday digital lives. From social networking and online banking to streaming services and productivity tools, web apps drive most of the online services we interact with daily. Companies depend on them like their scalability, easy access, and cost efficient deployment. But, not all types of web applications are the same there are various kinds, each designed like special purposes, technical needs, and user experiences.
In this article, we’ll get a near look at the main types of web applications, highlighting their advantages, disadvantage, and the situation where each performs best.
As you know you are a developer, business owner, or simply interested in technology, this guide will help you find which web app model suits your needs most efficient.
What are Different Types of Web Applications? Examples & Use Cases
Here are the 11 Types of web applications, each are the different unique features and use cases:
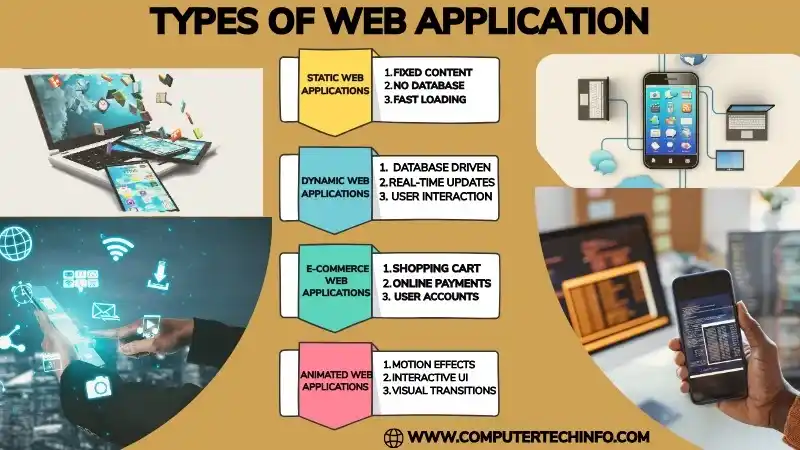
a). Static Web Applications
These are the most basic websites, built with HTML and CSS, perfect like presentations or digital brochures.
Their content remains the same unless a developer updates it manually.
Also Read: What is Webcam in Computer? Types, Uses, and Working
Static web applications are easy to create and host since they don’t need complex server side processing.
Advantages
- Fast loading speed
- Easy to host and deploy
- Low development cost
- Highly secure due to minimal server interaction
Limitations
- Poor scalability for dynamic content
- Limited user interaction
- Requires manual updates for content changes
b) Dynamic Web Applications
Dynamic web applications are more advanced and highly shared.
They use both client side and server side scripting such as HTML, CSS, JavaScript, PHP, ASP, or JSP to update content immediately.
These applications are connected to a database, enabling customize content based on user actions and liking.
They are perfect like businesses that focus on user engagement and daily changing content.
Due to their difficulty, dynamic web apps are more hard to develop and maintain.
They also need stronger hosting environments and normally come with higher development costs.
Advantages
- Supports real-time data
- Highly interactive
- Easy to integrate with databases
- Flexible and scalable
Limitations
- Slower than static apps
- More complex development
- Security concerns due to server-side logic
c). Single-Page Applications (SPAs)
A Single Page Application (SPA) runs on one HTML page and updates content actively as the user connect latest.
These applications are various important platforms where speed and smooth user experience matter, such as:
• Social media sites
• Email services
• Cloud-based tools
The biggest advantage of SPAs is that they do not reload the complete page after each action, allowing users to navigate fastly and smoothly.
Also Read: What is Difference Between CPU and GPU? GPU Vs CPU
However, they also have drawbacks especially in SEO and first load time, now the entire application loads at once.
SPAs are normally built with JavaScript frameworks like Angular, React, or Vue.js, which handle content updates and interface, provide easily.
Advantages
- Fast and smooth user experience
- App-like performance
- Reduced server load
- Enhanced interactivity
Limitations
- SEO challenges (unless SSR is used)
- Longer initial load time
- Complexity in development
d). Multi-Page Web Applications (MPAs)
Unlike SPAs, Multi Page Applications (MPAs) reload the complete page alike the server every time a user execute an action.
These applications are perfect like websites that handle large amounts of content and multiple features, such as:
• eCommerce platforms
• Online catalogs
• Educational portals
MPAs are better at managing complex structures and big databases compared to SPAs.
They also perform well in SEO, as each page able to be indexed individually by search engines.
However, MPAs capable of feel slower and require more resources, as each new page load triggers a server request.
Building MPAs many time demands a more detailed back end structure to support multiple pages and interactions.
Working with a skilled web development team capable of help ensure smooth capability and a strong online presence.
Advantages
- Better SEO support
- Easier to scale with many pages
- Well-suited for large websites
Limitations
- Slower navigation
- More complex backend
- Longer development time
e). Progressive Web Applications (PWAs)
As you know, Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) are mix of familiar websites and mobile applications.
They able to be installed directly onto a device’s home screen without using an app store and offer features like:
• Offline access
• Push notifications
• Background data syncing
PWAs are responsive, shareable via URL, and easy to access over different devices.
They deliver fast performance, smooth animations, and smooth scrolling like a native app local like feel.
Because they run effectively even with limited internet, they are perfect like users with weak or variable connectivity.
Developers build PWAs using standard web automation such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
Advantages
- Offline functionality
- Lower development cost compared to native apps
- Can be added to home screens
- Improved performance using caching
Limitations
- Limited access to device hardware
- Not fully compatible with all browsers
- Cannot perform like high-end native apps
f). Content Management Systems (CMS)
Content Management Systems (CMS) are best like blogs, e-commerce websites, and news portals so content needs to be updated daily without need deep technical knowledge.
Popular CMS platforms such as WordPress, Joomla, and Drupal provide a wide area of templates and plugging like easy customization.

They involve the simple, user friendly dashboards that build it easy to publish, edit, and arrange content effectively.
Advantages
- User-friendly
- Fast development
- Huge plugin ecosystems
- Easy content updates
Limitations
- Can be slow if overloaded with plugins
- Requires regular security updates
g). e-Commerce Web Applications
E-commerce websites are advanced systems that combine multiple features such as:
• Product listing and catalogs
• Search and filtering options
• Shopping cart system
• Secure payment processing
• Customer accounts & order management
• Customer support and service tools
These applications must be easy to use and offer a smooth shopping experience so customers stay busy and return.
They must be scalable sufficient to handle high traffic and big sales volume.
Also Read: Differences between Internet and Intranet | Internet Vs Intranet
Security is important to save easily affected customer information like payment details.
Liked e-commerce platforms Shopify, Magento, and WooCommerce.
These applications have change the sales industry, permit businesses to achieve broad audiences and work 24/7.
Advantages
- Supports high traffic
- Secure transactions
- Scalable stock management
Limitations
- Complex development
- High security requirements
- Requires continuous updates
h). JavaScript-Powered Web Applications
JavaScript is a flexible and popular used programming language that helps create dynamic and interactive web applications. Based on, to a analytical report released on February 6, 2025, JavaScript was the most commonly used programming language in 2023. It supports real time updates, animations, and interactive UI features, building it a core tool like modern web development.
JavaScript works on both frontend and backend, which builds it highly valuable like full stack development.
Web applications built with JavaScript are fast and efficient, as they capable of refresh content instantly without reloading the entire webpage.
This capability builds JavaScript ideal like building:
• Social media platforms
• Online gaming applications
• Collaboration and productivity tools
• Framework-based apps using Angular and Vue.js
i). Rich Internet Web Applications (RIAs)
Rich Internet Applications (RIAs) are web applications designed to offer a desktop like experience directly within the browser.
They use client side frameworks to enable smooth interaction and a richer interface, such as:
• Adobe Flash
• JavaFX
• Microsoft Silverlight
RIAs work inside the browser but behave like desktop software, supporting fast interaction, visual elements, real time operations, and advanced data presentation.
They capable of process data and perform tasks on the client side without contacting the server every time, which reduces loading delays and enhances performance.
However, RIAs often need specific plugins or frameworks, which may limit availability and similarity arond browsers and devices.
Advantages
- High interactivity
- Smooth, desktop-like experience
- Rich media support
Limitations
- Browser compatibility issues (for older frameworks)
- Heavy resource usage
j) Portal Web Applications
PAWs act as gateways that provide access to multiple services, information, and applications alike one place.
They are commonly used by organizations to control internal workflows as well as customer facing services effectively.
These applications support features like user authentication, personalized content delivery, and centralized resource access, build them highly useful.
PAWs collect and organize content alike different sources, ensuring users get a smooth, unified, and merged experience
They are capable of handling various functions, including:
• Search engines
• Email services
• Discussion forums
• News feeds
Advantages
- Centralized information
- Personalized experience
- Multi-user role access
Limitations
- Complex architecture
- Higher development and maintenance cost
k). Animated Web Applications
These applications focus on visually rich content and responsive experiences, many time using animations to engage users.
They are commonly used in areas where high user involvement is needed, such as:
• Online advertising
• Gaming platforms
• Educational tools
These web applications depend on CSS3, HTML5, and WebGL to create up to date and visually dynamic interfaces.
Their attractive visuals help capture user notice and increase overall interaction and service.
However, developing such applications that are able to be time consuming and needs strong design and programming expertise.
It is important to make sure animations support the user experience compare than confuse it, support performance and availability around devices.
Conclusion
Web applications exist in various forms, each designed to serve different purposes and business goals. Whether it’s a simple website like information or a highly interactive platform, as you know the types of web applications helps in choosing the best solution for performance, scalability, and user experience.
Also Read: What is Difference between Router and Modem? With Examples
With choice ranging alike static sites to SPAs, MPAs, PWAs, and advanced portal based systems, the modern web offers solutions like nearly every need.
Choosing the right model ensures your application runs smoothly, remainder user friendly, and supports long term growth.



