What is CPU Register?
Definition: Register is a temporary storage memory that built into processor (CPU). In the Computer Architecture, registers are special types of computer memory which performed their tasks quickly such as (Fetching, transferring, and storing) data and instructions.
Register memory is smaller compare to other computer memory like as Main Memory, Secondary Memory, and Cache Memory.
All computers required these registers to manipulate data, and store memory addresses. Main objective of using memory addresses is to identify the next instructions that to executed, after completing execution of the currently instruction.
Types of CPU Registers and Their Functions
Here, we will discuss about different types of CPU registers with their functions which played vital role in the Computer Architecture. Below explain each one –
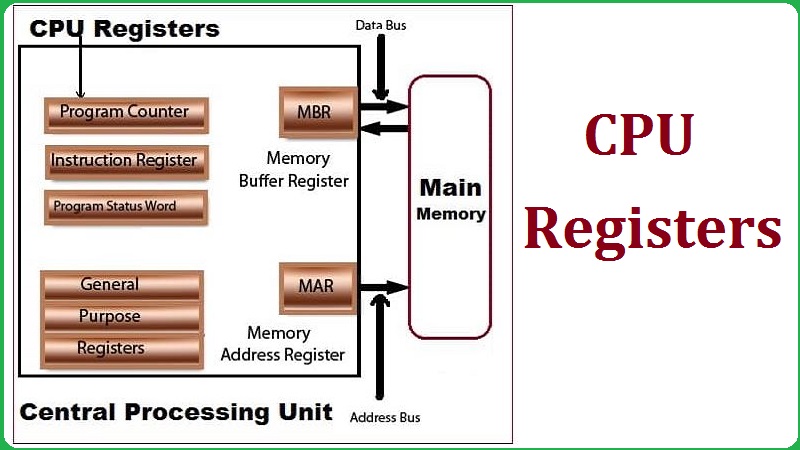
MAR Register
MAR stand for “Memory Address Register”, and its main objective is to store all memory addresses of entire data and instructions. This MAR helps to make the communication with using of MDR (Memory Data Register) in between the CPU and Main Memory.
For example – If, CPU (Center Processing Unit) needs to hold few data in to Primary Memory otherwise to fetch some data from memory side. Then, it places those addresses that needed into main memory in the MAR (Memory Address Register).
PC Register
PC stands for “Program Counter” register, and it is also known as Instruction Pointer (IP) in the Microprocessors. But, sometimes few people is known as named with “Instruction Address Register”.
Program Counter register’s function is to hold all records in sequence of entire execution of programs. PC has the memory address of further instruction that fetched in next step.
PC registers to keep track the address of next instruction which to fetch from the primary memory, if recently instruction completely executed. It helps to count all numbers of entire instructions.
MDR Register
MDR stands for “Memory Data Register“, and this register needed after completing the execution in PC register. CPU fetches some mandatory instructions and data from main memory side. Then, its temporary copy saved into this data register before decoding this data. So, MDR register works as a middle buffer
AC Register
AC register has another name the “Accumulator Register“, because this register holds the integer values. They have to need by the ALU (Arithmetically Logical Unit) while executing of any specific instruction.
Main function of Accumulator Register is to store the output which generated by your system. When CPU will execute some instruction then it will produce the result, now AC register get need to store those produced data.
Index Register
Index register helps to update operand while running of the programs in the computer’s CPU.
MB Register
MB register stands for “Memory Buffer Register“, and this register contains the information of data or instruction which read or written in main memory.
So, Memory Buffer Register’ function is to hold all data and instruction that are fetching or going to the primary memory side.
Data Register
Mostly, these types of register embedded into microcomputers for temporary storing data transmitted or from other peripheral devices.
AR Register
AR stands for “Address Register“, and its main function is to hold the memory location of instruction that executed. This AR register contains the six registers with named (CS, DS, ES and SS, FG, GS).
IR Register
IR stands for “Instruction Register“, and this register uses to store those data which needed in currently execution period.
IPR Register
IPR “Instruction Pointer Register“, and main function of this register is to hold memory location that executed in the next level. So, IP register stores the sequence of all instructions to performed.
SCR Register
SCR “Stack Control Register“, and it is pre set memory location in which data get save and retrieved in the specific order LIFO (Last-In-First-Out).
Main function of SCR Register is to handle the stack in the Computer System. To manage stack functionality, to use two special registers (SP and BP).
FR Register
FR register stands for “Flag Register“, and this register helps to indicate the specific condition. Flag register contains the one or two bytes, and further every byte get split into 8 bits. And every bit delivers the flag means condition.
Few flags register are Carry flag, Parity flag, Sign flag, Zero flags, and Overflow flag.
GPR Registers
GPR stands for “General Purpose Registers“, and these are unified types of registers. These registers are capable to store the memory addresses, data values as well as floating-point values. Mostly, GPR registers are using into modern CPU and GPUs due to their best flexibility.
SPR Register
SPR stands for “Special Purpose Registers“, that used to hold the program state. These SPR registers are enabled with PC (Program Counter) and SR (Status Register).



