What is Virtual Memory?
Definition: Virtual memory that means an large secondary memory of operating system, and it allows to hardware and software of computer system to support for physical memory on transferring time of data from main memory to secondary memory such as hard disk.
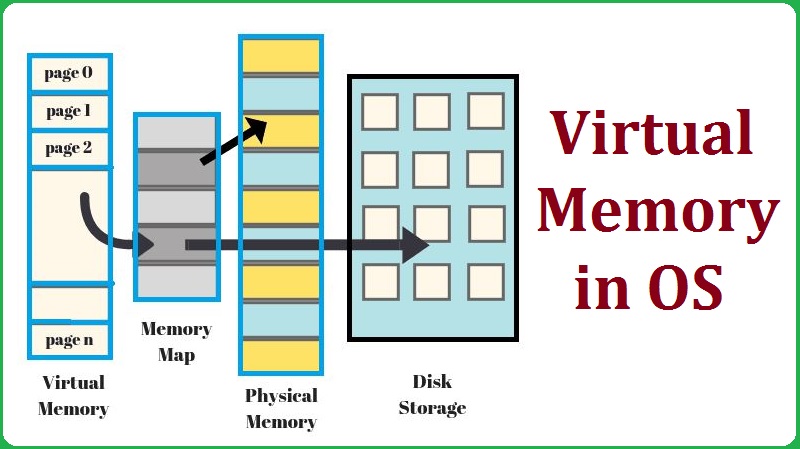
Virtual Memory Diagram
Due to move virtual memory into physical memory, operating system splits own memory into different blocks with fixed number of addresses. And those blocks has name the “Page files or Swap files”. All pages get reserve in the hard disk, and OS moves it from hard disk to primary memory, when they are needed, and finally virtual addresses translate into real addresses.
Need of Virtual Memory
- Main objective of needing is virtual memory is to increase the storage space of running memory, without adding any external memory such as RAM (Random Access Memory).
- If, any time computer’s physical memory totally occupied for other programs, but same time it needs to some extra memory then requests get forward to hard disk for swapping files like as virtual memory.
- If, any time computer requires the extra more main memory (RAM), then it try to install in the machine, and it works as small area of disk for fulfill system needs.
Types of Virtual Memory
Entire memory operations of computer get managing by the memory management unit (MMU), and enabled with handling Virtual Memory. Memory management unit allows embedding in the CPU (Center Processing Unit).
Virtual Memory is managed with two techniques such as Paging and Segmentation.
Paging
In this way, memory divided into different small blocks with near about 4 KB in size, and these blocks are known as Paging Files.
The paging is enabled with using the page table, which is help out to translate the virtual addresses for using operating system and other running other applications. Ad they use those addresses into physical addresses which used by MMU.
When, operating system and other currently using applications are not able to find appropriate address, which are located into RAM, then memory management unit try to response for missing memory reference along page fault. But if Page occurs into RAM, then its virtual address exists into page table.
Segmentation
Main objective of using the Segmentation is to handle the virtual memory. In this process, virtual memory divided into various different segments. But these segments are not using into memory because those segments transfer in the virtual memory on hard drive. Segment table keeps all records of entire information of whole segments.
Sometime virtual memory system tries to merge the paging and segmentation, and after getting combinations of then memory divides into pages or frames.
How Virtual Memory Works?
Now these days, virtual memory is very common word. Virtual memory is very helpful, when anyone page needs to load into primary memory for its execution, but it has not enough memory for those pages.
Then, virtual memory helps to short out that issue such as – lack of memory.
Now, here we will explain the working of virtual memory with suitable example. Like as –
Example of Virtual Memory
- Suppose, if operating system requires the 200 MB memory’s space to manage the all programs, which are working in currently.
- But, at present having only 100 MB physical memory space that stored on the Random Access Memory (RAM).
- Then, Operating system will try to create the 200 MB of virtual memory, and VMM (Virtual Memory Manager) helps to handle that memory.
- VMM has to work to arise the new files on the hard disk, which are need (100 MB) such as (200 MB-100 MB) = 100 MB.
- VMM has responsible to deal in real memory, which is only 100 MB.
Advantages of Virtual Memory
There are several of pros/benefits of enabling virtual memory, such as –
- Assigning the memory is very cheap and effective way.
- Page mapping done good manner.
- Virtual memory helps to trash the external fragmentation.
- While using of huge virtual space, vast programs can implement.
- Virtual memory allows too fast and easy processes.
- Due to store of programs in the virtual memory, not need more memory space.
- All data (page frames) can distribute on the entire physical memory.
- Allowing the very effective swapping
- It allows the multi programming environment.
- It is capable to operate multiple applications concurrently.
- It allows the flexibility because their large programs can fit into small size programs.
- It allows sharing common data between their memories.
- All processes can get large size to physical memory.
- It allows reading all data from hard disk, when to need.
- It allows replacing any code in physical memory without needing relocation.
- It helps to improve the performance of CPU.
- It has no any boundary for all degree of multi programming.
- It allows huge virtual address space to physical memory.
- It allows allotting the specific segment of program for execution of particular program, so it helps to enhance the speed of execution time.
- It allows the protection between two programs.
Disadvantages of Virtual Memory
There are some limitations of virtual memory such as –
- While using of virtual memory, all application’s speed are getting slow.
- It consumes more hard disk space.
- Lack of system stability
- It is not capable to deliver the equal performance like as RAM.
- Due to virtual memory, system gets degrade.
- It consumes more time between switching the applications.
- Increase the software complexity and hardware cost.
- Required the best hardware support
- Kernel developers require a profound understanding of the hardware, if they are using Virtual memory.




